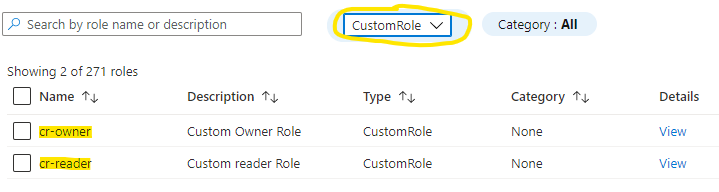
My recommendation for managing IAM in Azure take into account using the built-in Role Based Access Control (RBAC) Role Definitions first. In reality, built-in roles don’t always make a perfect fit. At that point we need to look at defining Custom Role Definitions to create a role based on the need.
I am not going to go into detail on Azure RBAC role definitions, or any specific actions/notActions. The configuration will depend on what you need. What I will cover is the creation and management lifecycle of a custom role definition.
There are a different options to create a custom role including:
| Azure Portal | Azure PowerShell | Azure CLI | REST API |
Any of these options could work for what I was trying to do. Instead I choose the road of using an ARM template to standardize the creation and long term management of custom roles.
ARM Template
The template for deploying a custom role definition isn’t too complicated. The role definition is a stand alone resource. All the role specifics will be defined with the parameter file(s).
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Authorization/roleDefinitions",
"apiVersion": "2018-07-01",
"name": "[variables('roleDegGUID')]",
"properties": {
"roleName": "[variables('roleDefName')]",
"description": "[parameters('roleDescription')]",
"type": "customRole",
"isCustom": true,
"permissions": [
{
"actions": "[parameters('actions')]",
"notActions": "[parameters('notActions')]"
}
],
"assignableScopes": [
"[concat('providers/Microsoft.Management/managementGroups/', parameters('tenantRootID'))]"
]
}
}
],
Assignable Scope
The important question that needs to be answered is where to deploy the role definitions. The role definitions can be deployed at the Management Group or Subscription level. The scope will determine where in Azure the role definition will be available for assignment. My recommendation is deploying to the Root Management Group, which will make it available everywhere in the tenant without needing to define any potential future scope.
To deploy to the Root Management Group you need to ensure you have assigned the needed permissions. By default ‘Owner’ permissions to the Root Management Group are not assigned out of the box. The follow PowerShell snippet will assign the needed permissions.
New-AzRoleAssignment -SignInName "[userId]" `
-Scope "/"`
-RoleDefinitionName "Owner"
Role Parameters
The secret sauce for this process is using an individual parameter file for each role definition. The only significant difference between the parameters are the ‘roleName’, ‘actions’ and ‘notActions’. Plug in the actions as needed to define the role.
"actions": {
"value": [
"*/read"
]
},
"notActions": {
"value": [
"Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/delete",
"Microsoft.Network/serviceEndpointPolicies/write",
"Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/*",
"microsoft.network/virtualnetworkgateways/*"
]
}
In this example I am creating a custom role to enable global read access with a few restrictions for specific network services that where read access is not allowed. A full list of available Azure resource provider actions is documented on Microsoft Docs - Azure Resource Provider Operations.
Deployment
In an attempt to make the deployment of multiple Role Definitions as easy as possible. I wrote a small PowerShell script that will iterate through all parameter files in the ‘role_definitions’ directory, and run a management group deployment. This can easily be integrated as is, or as part of your deployment automation tool of choice.
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][string]$parameterPath = ".\role_definitions\",
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$tenantRootMG,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][string]$azLocation = "centralus"
)
# Import custom role definition ARM parameter file(s)
$roleDefinitions = (Get-ChildItem -Path $parameterPath | Where-Object {$_.name -like "*parameters.json"}).fullname
$roleDefinitions | ForEach-Object {
New-AzManagementGroupDeployment -ManagementGroupId $tenantRootMG `
-Location $azLocation `
-TemplateFile .\azCustomRole.azrm.json `
-TemplateParameterFile $_ `
-tenantRootID $tenantRootMG
}
Note: This deployment will be done at a management group (New-AzManagementGroupDeployment).
After the deployment is completed you can check the Azure Portal for custom RBAC roles to see the definitions.